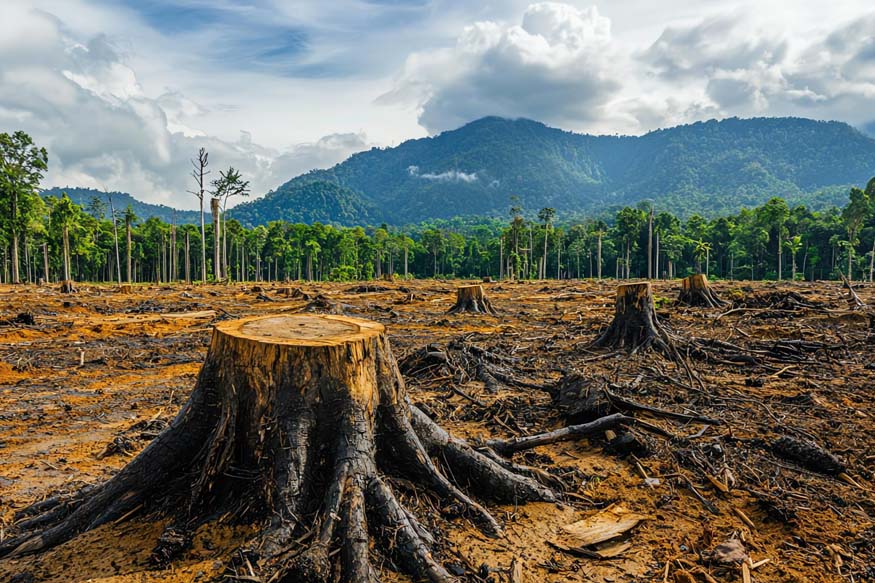
Forests cover about 31% of the land area on our planet. This land area is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species and plays a crucial role in the balance of our ecosystem. Human activities are causing unprecedented rates of forest destruction, leading to a phenomenon called deforestation. Understanding deforestation and its causes and effects is essential for developing effective strategies to combat this environmental crisis.
Understanding what deforestation is
Deforestation refers to the large-scale removal of forested land for non-forest use. This process often involves clearing trees for agricultural activities, urban development, or logging. Forests play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by regulating the climate, conserving biodiversity, and supporting the livelihoods of millions of people. The constant loss of forests worldwide poses a significant threat to the environment and human well-being.
Causes of Deforestation
Several factors contribute to the ongoing deforestation crisis. Here are some examples of the causes of deforestation.
Agricultural Expansion: As the global population grows, there is an increasing demand for food, which leads to the conversion of forests into agricultural land. This includes subsistence farming and commercial agriculture, such as palm oil, soy, and cattle ranching.
Logging: Commercial logging for timber, paper, other paper, and other products contributes significantly to deforestation. Illegal logging further exacerbates the problem by bypassing environmental regulations and sustainable practices.
Infrastructure Development: The construction of roads, highways, and urban areas often requires clearing forests. This not only directly damages trees but also opens previously inaccessible areas to further exploitation.
Mining: Extractive industries such as mining for minerals, oils, and gas can result in significant deforestation. The removal of vegetation and soil for mining operations disrupts the ecosystem and releases stored carbon into the atmosphere.
Climate Change: Changing climatic conditions can also exacerbate deforestation. Increased frequency and intensity of wildfires, droughts, and storms can weaken forest resilience and make them more susceptible to deforestation.
Effects of Deforestation
The consequences of deforestation are far-reaching. Here are some of the effects of deforestation.
Loss of Biodiversity: Forests are home to millions of plant and animal species. The destruction of these habitats leads to the loss of biodiversity and threatens the survival of many species.

Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When trees are cut down, the stored carbon is released, contributing to increased greenhouse gas emissions and global warming.

Soil Erosion: Trees and vegetation help to stabilise the soil and prevent erosion. Deforestation removes this protective cover, which leads to increased soil erosion and degradation of the land.

Water Cycle Disruption: Forests play a vital role in regulating the water cycle by maintaining humidity levels and influencing rainfall patterns. Deforestation can disrupt these processes, which leads to changes in precipitation and water availability.
Impact on indigenous communities: Many indigenous communities depend on forests for their livelihoods, culture, and traditions. Deforestation can displace these communities and threaten their way of life.
Types of Deforestation
Deforestation can be classified into several types based on the methods used and the extent of forest loss:
Clear-cutting: This method involves the complete removal of all trees in a specific area. It is often used in commercial logging and agriculture, but has severe environmental impacts.

Selective logging: In this method, only specific trees are removed, leaving the rest of the forest intact. While it is less destructive than clear-cutting, selective logging can still harm the ecosystem if not managed sustainably.

Slash-and-burn agriculture: This traditional farming method involves cutting down trees and burning the vegetation to create fertile land for agriculture. It is common in tropical regions but can lead to rapid deforestation and soil degradation.
Fragmentation: This occurs when large, continuous forests are broken up into smaller patches due to human activities. Fragmentation can isolate wildlife populations and reduce their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
Prevention of deforestation
Preventing deforestation requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes sustainable alternatives:
Land use planning: Developing and implementing land use plans that balance economic development with environmental conservation can help prevent deforestation. This includes designating protected areas and promoting sustainable agriculture and forestry practices.
Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of forests and the impacts of deforestation can inspire individuals and communities to take action. This includes promoting environmental education in schools and public outreach campaigns.
International cooperation: Deforestation is a global issue that requires coordinated efforts from governments, organisations, and individuals worldwide. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, can help address the drivers of deforestation and promote sustainable development.
Deforestation is a pressing global issue that demands urgent action. By understanding deforestation, its causes, and its effects, we can develop and implement effective strategies to combat this environmental crisis. Promoting sustainable practices, supporting reforestation efforts, and raising awareness are crucial steps in preserving the world’s forests. Through collective efforts, we can mitigate the adverse effects of deforestation and ensure a healthy and balanced ecosystem for future generations.

At Center Point School, we believe in the importance of environmental conservation and education. By instilling a sense of responsibility towards the planet in our students, we aim to foster a generation that values and protects our natural resources. Through various initiatives and programs, we are committed to raising awareness about deforestation and its impact, empowering students to become proactive stewards of the environment. Together, we can create a sustainable future for both people and the environment.